Table of Contents
It's easy to create 3D printable objects with MeshUP! Let's take a quick look at how to use the essential tools.
When you want to learn more, see tutorials for new guides and video walkthroughs.
The Interface
Navigation
X axis: red
Y axis: green
Z axis: blue (Note: Z is up)
Move the camera view around the model
Windows: left mouse button:
Mac: click and hold with the left finger while another finger slides around the trackpad
Pan the camera view horizontally or vertically
Windows: right mouse button
Mac: two finger click and hold while sliding around the trackpad
Zoom in and out: middle mouse button
Windows: middle mouse button
Mac: two finger slide up and down the trackpad (do not click)
Menu
File
Open files
Import any STL, OBJ, PLY or MUP file.
Open stock files
Open files from our library of models and templates.
Save objects
Save all objects in the scene as a MUP file.
Save selected objects
Save selected objects (not all objects in the scene) as a MUP file.
Export objects as a mesh
Export all objects in the scene as a mesh.
Export selected objects as a mesh
Export selected objects (not all objects in the scene) as a mesh.
Edit
Undo
Undo the previous action.
Redo
Redo the previous action.
Copy
Duplicate the selected object in place.
Copy can also be achieved by typing C or Command C.
Delete
Delete the selected object.
Delete can also be achieved by hitting the Delete key on your keyboard.
Repair
Repair holes
There are 3 hole types, Hard and Soft.
- Crack fixes small holes and is recommended to try first.
- Hard is the default type of hole repair, which closes the hole in a flat style.
- Soft hole repair closes the hole in a rounded style.
Fix surface deformations
Check your property box and fix the types of errors shown for selected model.
- Intersection
- Degenerate
- Separate
Volume
Volumes are the base of MeshUP. All meshes imported must be converted to one type of volume before you can preform any operation, except Mesh Repair. There are 3 types of volumes to choose from:
Create volumes from meshes
- Envelope: this will work with any mesh, even polygon soup! Envelope can be thought of as inflating the object with air. The higher the offset, the more fine detail you will lose.
Note that we will calculate the smallest possible offset for the selected mesh. Check the bottom toolbar alert for this number. - Shell: requires the mesh has no intersections, degenerates, flipped faces, cracks but it can have holes. Shelling produces a one sided offset and can be thought of as a single sided envelope. Shelling preserves the positive normal surface, so on one side you get the exact surface, on the side the offset is applied.
- Volume: requires the mesh to be completely manifold: no intersections, degenerates, flipped faces, cracks or holes.
Union
Select 2 objects to join together. To also blend the objects together, add a value that is not 0.
Subtract
Select 2 objects, the second object will be remove from the first object. To add a blend between these two objects, add a value that is not 0.
Intersect
Make sure 2 objects intersect. Select these 2 objects and the result will be only the intersection between the two. To add a blend between these two objects, add a value that is not 0.
Replicate
Array object
Choose how many objects to copy in X, Y and Z and the distance between them.
Create a ring of objects
Coming soon.
Help
Help
Loads a tab with the wiki help system for MeshUP.
Bug report
Report a bug with the MeshUP team.
Properties Box
This box provides useful information about whatever is selected.
Name
The name of the object.
Object Type
Mesh or Volume.
All imported meshes must be converted into one of our volume types before performing operations. See the Volume Options section to know which options are possible with the current unrepaired mesh.
Shells
The number of unconnected meshes.
Mesh Defects
- Degenerate faces
- Flips
- Intersections
- Holes
Volume Options
All meshes must be converted to one of our volume options before preforming any operations.
- Envelope: this will work with any mesh, even polygon soup! Envelope can be thought of as inflating the object with air. The higher the offset, the more fine detail you will lose.
- Shell: requires the mesh has no intersections, degenerates, flipped faces, cracks but it can have holes. Shelling produces a one sided offset and can be thought of as a single sided envelope. Shelling preserves the positive normal surface, so on one side you get the exact surface, on the side the offset is applied.
- Volume: requires the mesh to be completely manifold: no intersections, degenerates, flipped faces, cracks or holes.
Bottom Toolbar
This toolbar has 3 important sections:
1) Gimbal
The left hand side has a toggle to turn on/off different parts of the Gimbal, and to change some of its settings:
- All: turn on translate, rotate and scale
- Translate
- Rotate
- Scale
- Snap (currently snap only works for Transform, not with Rotate and Scale)
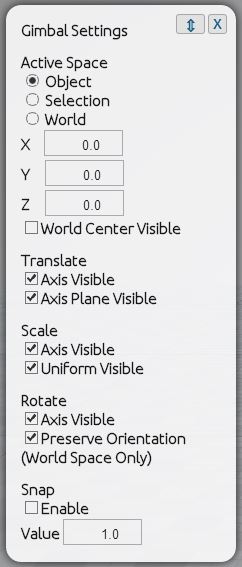
Also note the Settings button which will bring up a dialogue box to modify some of the settings of the Gimbal.

2) Coordinate system
Next to the translate, rotate, scale, and snap check boxes is a toggle for Local, World (selection center) and World (World center).
- Local: Including origin point and angular position in reference to the universal coordinate system. In simpler terms this means the local origin point of the currently select object(s).
This is the default coordinate system of MeshUP.
- World (Selection center) : The local coordinate system with 0,0,0 at the center of the selected object and has been axis-aligned to the world coordinate system.
- World (World center) : The local coordinate system with 0,0,0 at the center of the world and has been axis-aligned to the world coordinate system.
3) Progress bar
The bottom right hand side of this toolbar will show an active progress of all commands. Multiple commands can stack up, as will each of their status bars.

4) Dash
The bottom row of this toolbar will display all alerts and errors, from all commands. Each line begins with a time stamp to help keep track of the errors. The arrow icon on the right allows expand this box and see all errors and alerts from the current session.
Gimbal
The pink sphere in the middle is the 0,0 location Transform
- Red triangle: moves the selected object on the X axis only.
- Green triangle: moves the selected object on the Y axis only.
- Blue triangle: moves the selected object on the Z axis only.
Rotate
- Red sphere: rotates the selected object on the X axis only.
- Green sphere: rotates the selected object on the Y axis only.
- Blue sphere: rotates the selected object on the Z axis only.
Scale
- Red cube: scales the selected object on the X axis only.
- Green cube: scales the selected object on the Y axis only.
- Blue cube: scales the selected object on the Z axis only.
Transformation in Plane
- Blue/green arrows: translates the model in X and Z axes.
- Grey/red arrows: translates the model in X and Y axes.
- Grey/green arrows: translates the model in Y and Z axes.
Uniform Scale
The box in the center of the Gimbal will scale the object uniformly.
Precise Transform, Rotate, Scale
Right click on either Transform, Rotate, Scale to bring up the Precise dialogue box.
This gives the option of entering precise units and the ability to choose how many axes this applies to, which can be used for uniform scale.
Also note the Settings button the bottom of the toolbar to modify the properties of the Gimbal.
Multi-select
Multiple models can be selected and operated on at a time. To select more than one model either:
- Press and hold the alt key while drawing a window around the objects with the left mouse button.
- Select one model, then hold down the shift key and left click more models.